Recently, a paper titled "Data mining-guided alleviation of hyperuricemia by Paeonia veitchii Lynch through inhibition of xanthine oxidase and regulation of renal urate transporters" has been published in the top journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Phytomedicine) by the team of Dr. Yanbei Tu from Jiangsu University and Professor Yanfang Li from Sichuan University (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155305).
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is a metabolic disorder marked by elevated levels of uric acid. In this study, a total of 225 traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions (comprising 246 herbs) for HUA/gout treatment were collected and then were statistically analyzed through a data mining approach to determine the common nature and use frequency of their composition herbs. The results revealed that the properties, flavors and meridians of the appearing herbs were mainly cold, bitter and liver, respectively, while their efficacy was primarily concentrated on clearing heat and dispelling wind.
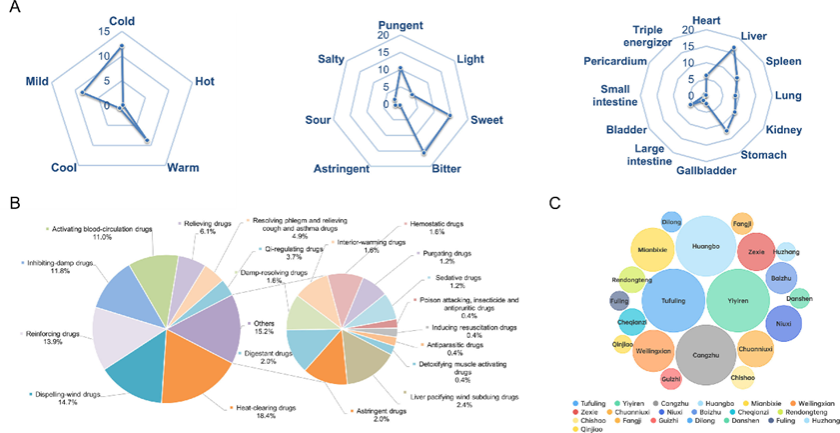
Fig. 1. Frequency analysis of herbs comprising the prescriptions. (A) Medicinal properties, tastes, and meridian tropisms of herbs. (B) Efficacy of herbs. (C) Medication
frequency of the top 20 herbs.
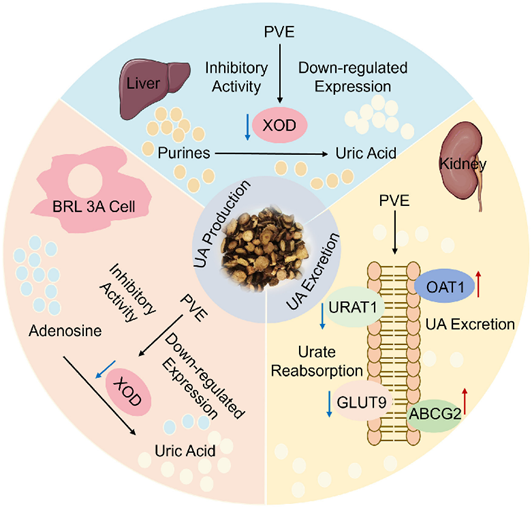
Following data mining analysis and experimental validation results regarding uric acid-lowering and xanthine oxidase (XOD) inhibitory activities, the researchers narrowed the focus of their study to Paeonia veitchii. They found that Paeonia veitchii extract (PVE) decreased uric acid production by inhibiting XOD expression and activity, and enhanced uric acid excretion by regulating renal urate transporters (URAT1, GLUT9, OAT1 and ABCG2). Through these mechanisms, PVE effectively mitigated hyperuricemia symptoms in HUA mice induced by potassium oxonate and hypoxanthine, and showed a favorable safety profile compared to the positive drug allopurinol. These findings underscore the potential utility of Paeonia veitchii in managing hyperuricemia and gout.
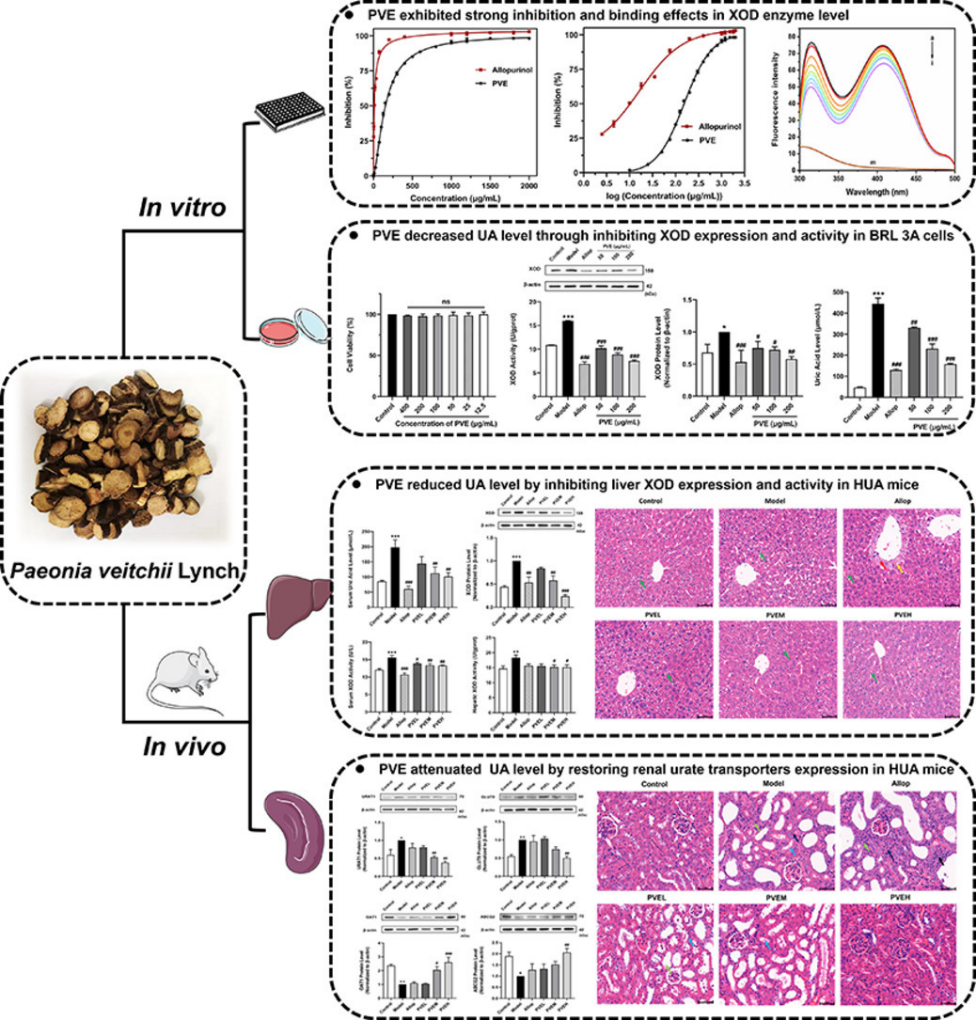
Figure 2 Schematic representation of PVE for the treatment of hyperuricemia
Associate Professor Yanbei Tu from Jiangsu University and Professor Yanfang Li from Sichuan University are the co-corresponding authors of this paper. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province in China (Grant No. 2022YFS0433); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82204724); the Senior Talent Foundation of Jiangsu University (Grant No. 5501290014).